My research empirically examines how households in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia are affected by environmental change and studies how they respond using panel surveys and geo-spatial data. Here are some projects I’ve been working on:
Exposure to floods, climate change, and poverty in Vietnam
(with Andrew Smith and Ted Veldkamp)

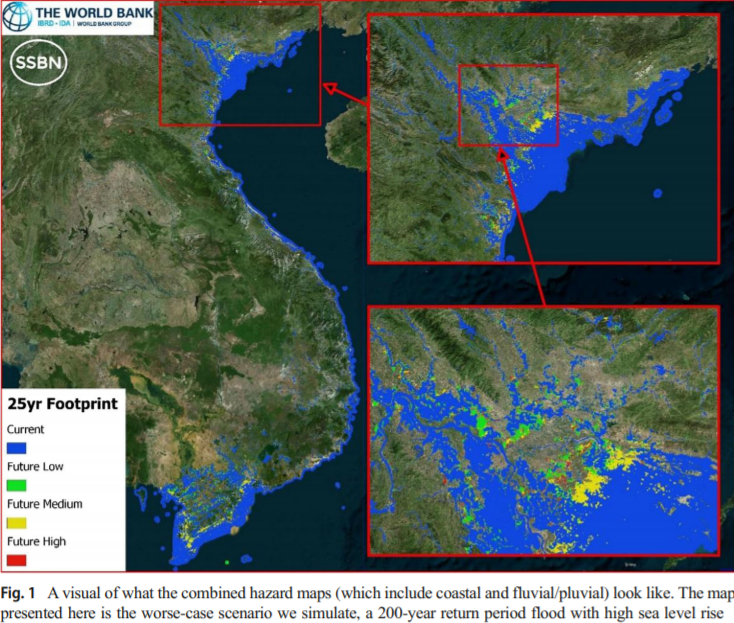
With 70% of its population living in coastal areas and low-lying deltas, Vietnam is highly exposed to riverine and coastal flooding. This paper conducts a “stress-test” and examines the exposure of the population and poor people in particular to current and future flooding in Vietnam and specifically in Ho Chi Minh City. We develop new high-resolution flood hazard maps at 90 m horizontal resolution, and combine this with spatially-explicit socioeconomic data on poverty at the country and city level, two datasets often kept separate. The national-level analysis finds that a third of today’s population is already exposed to a flood, which occurs once every 25 years, assuming no protection. For the same return period flood under current socioeconomic conditions, climate change may increase the number exposed to 38 to 46% of the population (an increase of 13–27% above current exposure), depending on the severity of sea level rise. While poor districts are not found to be more exposed to floods at the national level, the city-level analysis of Ho Chi Minh City provides evidence that slum areas are more exposed than other urban areas. The results of this paper provide an estimate of the potential exposure under climate change, including for poor people, and can provide input on where to locate future investments in flood risk management.
The multifaceted relationship between environmental risks and poverty: new insights from Vietnam (with Ulf Narloch)

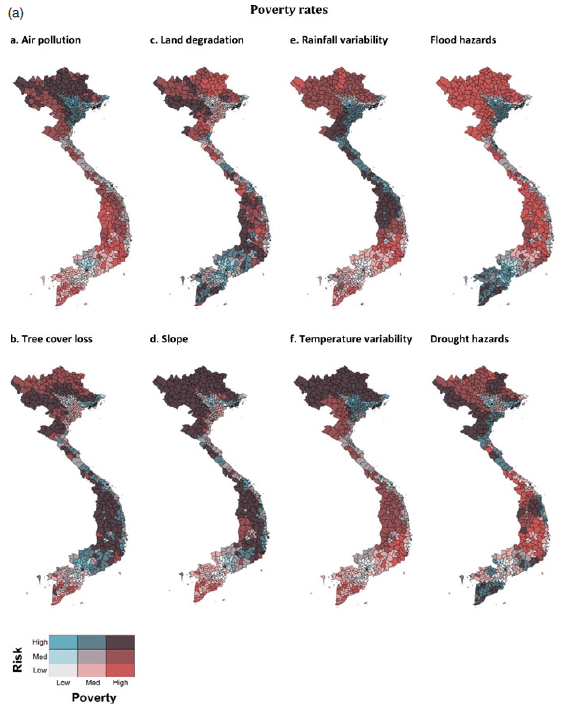
Despite complex interlinkages, insights into the multifaceted relationship between environmental risks and poverty can be gained through an analysis of different risks across space, time and scale within a single context using consistent methods. Combining geo-spatial data on eight environmental risks and household survey data from 2010–2014 for the case study of Vietnam, this paper shows: (i) at the district level, the incidence of poverty is higher in high risk areas, (ii) at the household level, poorer households face higher environmental risks, (iii) for some risks the relationship with household-level consumption varies between rural and urban areas, and (iv) environmental risks explain consumption differences between households, but less so changes over time. While altogether these analyses cannot establish a causal relationship between environmental risks and poverty, they do indicate that Vietnam’s poor are disproportionally exposed. Given growing pressures due to climate change, addressing such risks should be a focus of poverty reduction efforts.
Land and poverty: the role of soil fertility and vegetation quality in poverty reduction (with Martin Heger and Gregor Zens)

The debate on the land–poverty nexus is inconclusive, with past research unable to identify the causal dynamics. We use a unique global panel dataset that links survey and census derived poverty data with measures of land ecosystems at the subnational level. Rainfall is used to overcome the endogeneity in the land–poverty relationship in an instrumental variable approach. This is the first global study using quasi-experimental methods to uncover the degree to which land improvements matter for poverty reduction. We draw three main conclusions. First, land improvements are important for poverty reduction in rural areas and particularly so for Sub-Saharan Africa. Second, land improvements are pro-poor: poorer areas see larger poverty alleviation effects due to improvements in land. Finally, irrigation plays a major role in breaking the link between bad weather and negative impacts on the poor through reduced vegetation growth and soil fertility.